
Editor’s note: This is the second post in a series that explores a range of topics about upcoming AI regulation, including an overview of the the EU AI Act and Palantir solutions that foster and support regulatory compliance when using AI. This blog post provides an overview on how Palantir AIP empowers organizations to meet some of their key compliance obligations through core capabilities available in-platform, with a special focus on High-Risk AI Systems. In-house legal and compliance readers in particular will find in it a useful digest of key considerations for their organizations.
Introduction
The rapid adoption of AI, including Generative AI, has driven policymakers worldwide to develop regulations governing the development and deployment of AI systems, particularly those impacting fundamental rights and safety. In the first post of this series, we provided an overview of one such regulation: the EU AI Act.
As these regulations mature, organizations will be responsible for implementing a wide variety of compliance requirements throughout the AI lifecycle. Palantir AIP empowers organizations to meet many key compliance requirements efficiently and effectively in two primary ways:
- Core Capabilities: AIP’s robust feature set empowers users to maintain compliance with key AI governance requirements as they implement analytical or operational workflows throughout the AI lifecycle.
- Custom Applications: AIP is designed to empower a diverse community of builders with a suite of powerful tools for use case development. These include application-building tools, workflow-building tools, integrated analytics tools, and developer tools — all of which can be leveraged to build custom applications for AI compliance.
In this blog post, we highlight AIP’s core capabilities that enable institutional compliance for organizations leveraging AI, focusing on three key themes emphasized by emerging AI regulations such as the EU AI Act: Data Governance, Risk Management, and Record Keeping. We’ll address custom applications in a future post.
Within each of these themes, Palantir AIP offers an integrated toolset that can assist customers in defining and implementing processes to meet compliance requirements effectively. This includes in-platform tools for tracking, maintenance, and continuous monitoring of AI applications leveraging LLMs and other advanced multi-modal AI models. Our approach enables customers to deploy AI solutions confidently, ensuring they are effective for their use cases and organizational outcomes, while tangibly advancing transparency and trustworthiness principles that align with the core requirements of emerging regulations like the EU AI Act.
Data Governance: The Cornerstone of AI Governance
We know from experience that AI systems hold significant promise for helping to address mission-critical challenges — from inventory entity resolution to infection risk alerting — in real-world settings. Unlocking this transformative potential hinges on integrating advanced AI models with high-quality, relevant data tailored to their operational environments. That’s why a robust data governance strategy is the foundation of any effective AI governance framework.
By enabling organizations to implement comprehensive data governance throughout the AI lifecycle, organizations can ensure that every stage — from data collection to model training and, eventually, model deployment — maintains the highest standards of quality and relevance. This enables AI systems to drive impactful outcomes while mitigating risks to fundamental rights and safety. In doing so, institutions are better positioned to ensure compliance with data governance requirements for AI systems. For instance, Article 10 of the EU AI Act mandates that “training, validation and testing data sets shall be subject to data governance and management practices.” Adhering to such regulations helps organizations maintain the integrity and efficacy of their AI initiatives.
Access Controls
Throughout every stage of the AI lifecycle, Palantir AIP empowers users to ensure that the appropriate individuals have the correct access to the necessary information. Security starts with identity, so AIP uses strong authentication methods like single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to confirm users are who they say they are.
Palantir AIP simplifies the process of organizing users into groups, whether managed internally or through an organization’s existing identity providers. Once verified, Palantir’s role-based authorization grants access for users and groups based on precise permissions, so that users interact only with the data that they are authorized to see. By clearly defining group boundaries and maintaining strict separation between different teams and resources, organizations can use AIP to help keep sensitive data compartmentalized and protected.
Additionally, AIP’s Markings feature adds mandatory controls, allowing administrators to require special permissions for users to find or access highly sensitive information. For cases requiring even more precise control, granular access controls allow organizations to define exactly who can access specific data and resources down to individual rows or columns using mechanisms like Restricted Views. This exceptional level of control ensures that sensitive or restricted information is accessible only to authorized individuals.
With Palantir AIP, organizations can foster collaboration among employees while confidently relying on a foundation of configurable access controls. Strict controls and thorough documentation of data access are essential for providers of high-risk AI systems. According to Article 10(5)c of the EU AI Act, providers of high risk AI systems must implement appropriate safeguards for handling personal data. Consistent and standardized access management empowers institutions to protect their most valuable assets and maintain compliance with emerging AI regulations, as well as other applicable security and data protection requirements.
Data Cleaning
Trustworthy AI applications are built on high-quality, reliable data foundations. Article 10 of the EU AI Act highlights the importance of data preparation processes, especially for training models used in high-risk AI systems. This regulation requires institutions to carefully consider operations such as labeling, cleaning, and aggregating their data.
Data cleaning is a process that involves refining and enriching datasets of all types (e.g., structured data, streaming data, media data, etc.) to produce high-quality information. Palantir AIP provides a suite of tools that enable users across the technical spectrum to conduct these data cleaning tasks. Applications like Pipeline Builder and Contour offer no-code environments for users to build and manage data pipelines without writing code. On the other end of the spectrum, Code Repositories provide pro-code environments where developers can implement custom data transformations. Additionally, Data Lineage offers an dynamic visual representation of all steps from raw data ingestion to the finalized dataset.
These tools not only assist users in performing the necessary data cleaning for their AI systems but also maintain records of these activities. This enhances transparency and supports adherence to compliance standards, as outlined in EU AI Act Article 11 and Annex IV. These sections of the Act emphasize the need for organizations to produce technical documentation demonstrating the architecture of the high-risk AI system, including data cleaning methodologies.
Mitigating Risk and Bias
Mitigating risk and bias in the use of AI models and tools involves multiple facets. In this section, we discuss various mitigation strategies to reduce risks related to data access and the testing and evaluation of models to mitigate bias, as outlined in Article 10(2)(f) and (g) of the EU AI Act, which explicitly require high-risk AI system providers to examine and implement measures to mitigate potential biases.
The Palantir Platform offers tools such as the Sensitive Data Scanner (SDS) to mitigate the risk of broad data access. SDS can be used to identify protected characteristics in datasets, marking them appropriately to protect the information from broad accessibility. By controlling access to sensitive attributes that could introduce bias — such as gender, age, or physical home address — SDS can help users handle this data more carefully and prevents these attributes from inappropriately influencing model outcomes. In tandem, administrators can require operational users to justify the processing of user-defined special categories of data through tools like the Checkpoints application. This helps users ensure that the use of sensitive data is deliberate and justifiable, reducing the risk of improper data processing. Users can also utilize obfuscation tools for enhanced encryption capabilities and bolstered data minimization best practices. Data minimization reduces the exposure of irrelevant or sensitive information that could contribute to biased results, thereby mitigating bias at the data level.
Palantir software empowers users to leverage AI models by providing robust tools for testing and evaluation to demonstrate confidence in model use cases before pushing them to production environments. It offers organizations the capability to manage and select LLM models of their choosing while offering the flexibility to develop custom machine learning models within the platform.
For LLM use, applications like AIP Logic allow non-technical users to create environments for building, testing, and releasing functions powered by LLMs. A key component of AIP Logic is its “Evaluations” feature, enabling organizations to test use cases, evaluate functions, and validate that the output aligns with industry standards. By rigorously testing models against diverse datasets and evaluation metrics, organizations can identify and correct biased behaviors at all stages of the AI lifecycle.
For models developed within the platform, customers can configure their own evaluation libraries to measure model performance, fairness, robustness, and other metrics. These customizable evaluation libraries enable users to assess model fairness explicitly, providing insights into potential biases and facilitating corrective measures.
Retention and Deletion
Many regulatory frameworks mandate that data should not be accessible once it is no longer needed for a valid purpose or when retention periods expire. For example, Article 10 (5)(e) of the EU AI Act requires high-risk AI systems providers to delete personal data once the bias has been corrected or the data has reached its retention period.
To address these requirements, the Palantir Platform offers methods to set retention rules, ensuring proper data removal within organization-defined timeframes. Importantly, Palantir software further allows lineage-aware deletions, ensuring the removal of specific datasets as well as related downstream information. This can be configured using the Data Lifetime application. This comprehensive approach to data management facilitates compliance with data retention and deletion regulations, further enhancing the robustness of your data governance strategy.
Risk Management: Transparency through Monitoring
As AI systems become more integrated into the critical operations of businesses, managing the associated risks becomes imperative. Certain regulations, like the EU AI Act, explicitly mandate organizations to establish a risk management program. Specifically, Article 9 of the EU AI Act requires risk management systems be implemented for high-risk AI systems, while Article 55 mandates providers of General-Purpose AI (GPAI) models to evaluate these models and identify and mitigate systematic risks. This section delves into how AIP’s features can help organizations understand the AI system lifecycle through systematic reviews and oversight of updates, aiding compliance with legal requirements.
Modeling Objectives
Palantir’s Modeling Objectives provide a structured framework to document and manage the risks associated with AI systems. This feature enables organizations to collaboratively evaluate models and ensure they pass predefined quality checks before being operationalized and pushed to production for broader adoption. Modeling Objectives also enables organizations to facilitate staged rollout and release management with Model Asset Versioning, providing a controlled environment to manage the use of AI models.
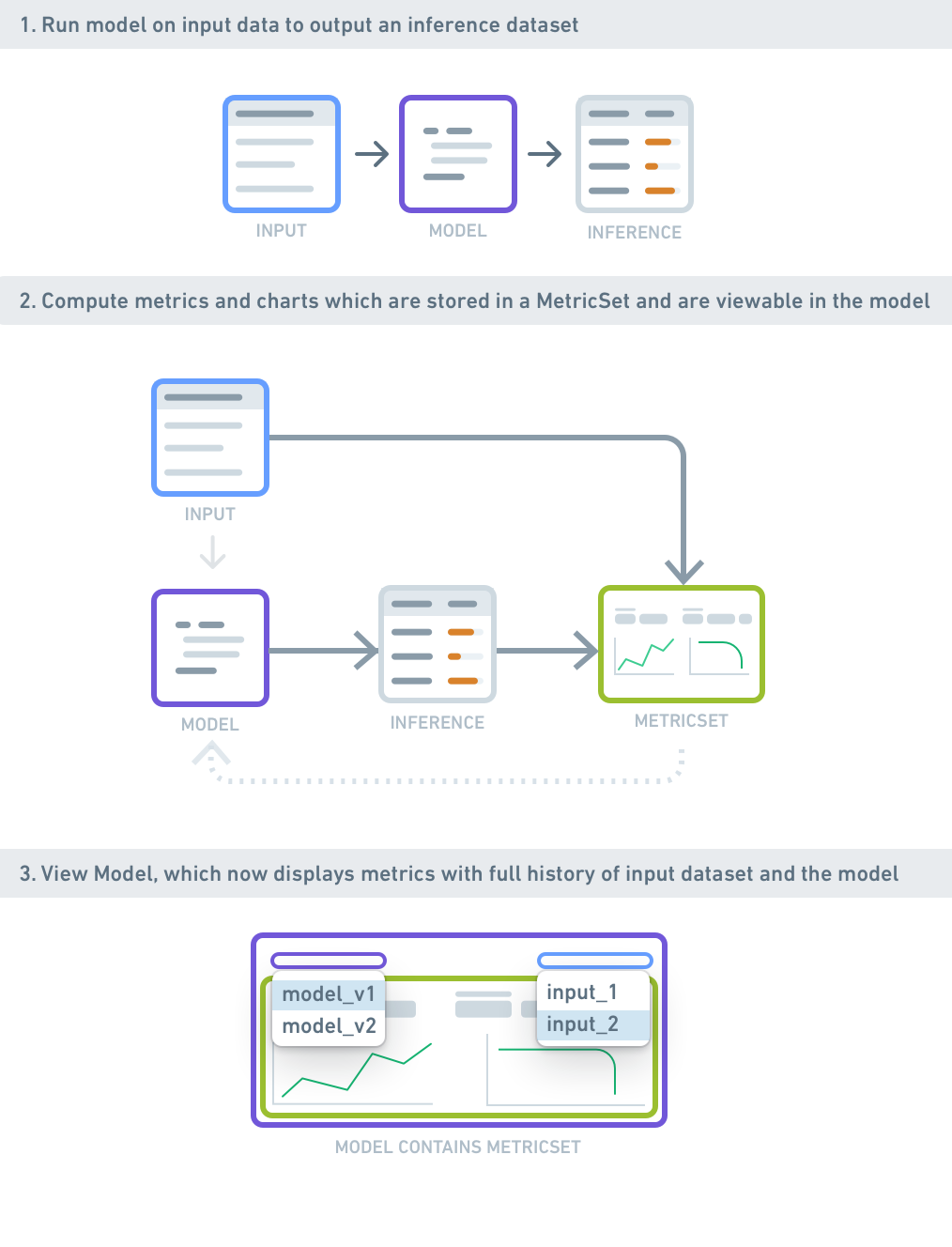
Model Catalog
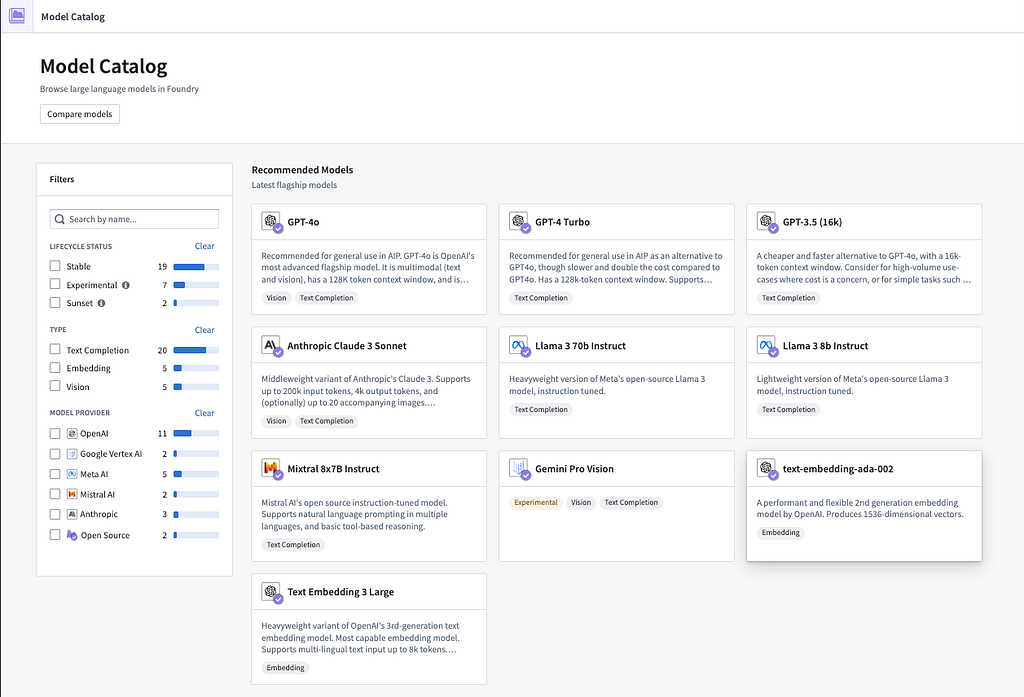
Organizations have the ability to create and test models within Palantir’s Platform and use the Model Catalog to access and review key characteristics of open-source models or those for which they already hold existing licensing. Furthermore, Palantir’s Platform enables organizations to integrate externally-hosted models stored in third-party applications, services, or model providers such as Azure Machine Learning, Amazon SageMaker, OpenAI, or Anthropic. Whether organizations choose to create or fine-tune their own models, use open-source ones, or integrate externally-hosted models, the Palantir Platform offers full versioning, granular model permissions, and governed model lineage. These features are designed not only to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of outcomes but also to significantly increase transparency.
Model Access Controls
Access controls within AIP are pivotal for targeted risk management measures, allowing administrators to manage who can build, evaluate, and interact with AI systems. Key features include:
- The ability to apply geo-restrictions to control where data processing occurs and who can interact with an AI system, ensuring compliance with local regulations.
- Granularly enabling or disabling specific model families based on organizational policies with Model Enablement Settings, ensuring that only approved models are used throughout AIP.
- Core access control primitives such as Groups and Markings enable granular control over who can access components of an AI system, from the training data to end-user applications.
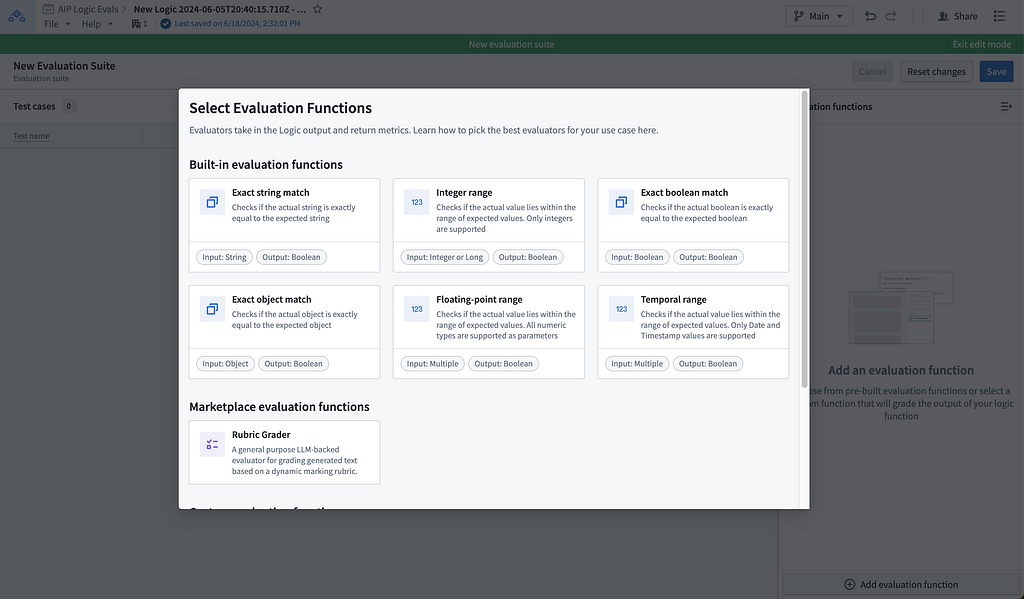
AIP Evals
AIP Evals is Palantir’s framework for transitioning AI prototypes into reliable production workflows. It emphasizes rigorous Testing and Evaluation (T&E) to ensure consistent and effective real-world performance. Designed for Generative AI, it handles non-determinism and specific input debugging. Through systematic reviews, unit testing, and continuous improvement, AIP Evals enables empirical validation and refinement of AI systems, ensuring transparency and trust for scalable, responsible AI deployment. One of our previous blog posts provides step-by-step guidance on creating a prototype AI system and taking it all the way to production.
Record Keeping: Accountability in AI Usage
AI systems are required to automatically record events throughout their lifespan and use. According to Article 12 of the EU AI Act, high-risk AI systems must support automatic record keeping of event logs and other critical logging capabilities. In this context, it’s important to note that audit logs from all Palantir platforms are generated and made available to customers with administrator access rights. These logs are initially written to disk and then archived to a environment-specific storage bucket within 24 hours (e.g., AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage, on-premises storage). Palantir customers have the option to enable audit infrastructure that exports audit logs from the archive to a per-organization dataset for analysis within the platform or a downstream SIEM. For more information on the monitoring of security logs, please refer to our documentation.
Monitoring Sensitive Workflows
Palantir offers tools that enable organizations to closely monitor their most sensitive workflows. This is particularly important when it comes to changes in the ontology, which are often viewed as highly sensitive due to the impact they can have on data interpretation and analysis.
The Palantir Ontology acts as a structured framework that organizes and interprets data, providing a shared vocabulary for different systems, applications, and users. This consistent ontology ensures seamless data integration from various sources, facilitating easy and unified data querying and analysis.
Action Logs and Modifications
Alterations to the ontology in Palantir’s Platform are primarily executed through ‘Actions,’ which can trigger associated downstream processes. These modifications usually stem from specific decisions. The Action Log feature streamlines the creation and maintenance of object types that represent these decisions. To visualize these Action Logs, Palantir provides customizable widgets within its platform, tailored to the needs of each organization. This capability allows organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of the broader context and decision-making processes behind ontology changes.
Edit Logs
Edit history meticulously logs all changes made to an object, detailing what was changed, by whom, and when. It tracks specific modifications to object properties, offering a focused record of edits over time. This level of transparency and control is crucial for maintaining data integrity and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Palantir has a long-standing commitment to upholding privacy-first principles. In addition to the development of new features, Palantir continually emphasizes the importance of robust auditing mechanisms. These mechanisms serve as a backstop to ensure that the features and users’ interactions with them can be reviewed as needed for consistency with institutional policies and regulatory requirements. This dual focus ensures that as the platform evolves, it remains in line with the highest standards of data privacy and transparency.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of AI compliance is an evolving challenge that requires robust and adaptive solutions. As regulations like the EU AI Act come into effect, organizations must be prepared to implement comprehensive compliance measures across the entire AI lifecycle. Palantir AIP stands out by offering a powerful combination of core capabilities and custom application tools that enable organizations to meet these stringent regulatory requirements efficiently and effectively.
By focusing on key themes such as Data Governance, Risk Management, and Record Keeping, Palantir AIP provides an integrated toolset that helps organizations define, implement, and monitor compliance processes seamlessly. The platform’s in-built tools for tracking, maintenance, and continuous monitoring ensure that AI applications, including those leveraging advanced models like LLMs, remain transparent and trustworthy.
In summary, Palantir AIP empowers organizations to innovate with confidence while adhering to emerging regulatory standards. Future posts will delve deeper into custom applications, illustrating how organizations can tailor their compliance strategies to meet specific needs. By adopting Palantir AIP, organizations are better positioned to advance their AI capabilities while maintaining rigorous compliance, setting a benchmark for responsible and sustainable AI deployment.
Authors
Annabelle Larose, Senior Technical Program Manager, Privacy & Civil Liberties Engineering
Colton Rusch, Privacy and Civil Liberties Engineer
AI Systems Governance through the Palantir Platform was originally published in Palantir Blog on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
